How to analyze your Sales CRM data
Introduction
CRM analytics provide you with information about your clients and how well your sales and customer support staff are doing. CRM analysis is useful for assessing customer experience, verifying customer records, monitoring customer behaviour, and more effectively producing leads. The advantages and different measures for conducting sales CRM research are explored in this blog.
What is CRM analytics?
CRM analytics are figures that show how well the business does in terms of revenue and customer service. CRM analytics also displays consumer information that can be used to make more informed business decisions. CRM platform is typically used to receive CRM analytics and automate both data collection and report generation.
Benefits of CRM analysis
The most important advantage of CRM research is that it will help you improve your pricing, customer support, and marketing processes. You will boost the processes by using CRM analytics in the following ways:
- Customer experience evaluations: CRM analytics provide you with information about the success of your customer service staff. Implement activities to drive the team toward these priorities if you see numbers that your team might change.
- Accurate consumer data: If you’re doing predictive marketing or email marketing, you need to know whether you’re meeting the right people. CRM reporting means that you are doing comprehensive consumer analytics.
- Effective lead generation: Your CRM research analysis will reveal which of your marketing efforts are most closely linked to sales. If you see that one solution is closely linked to transactions, but you’ve just hit a small percentage of your buyers with it, check it out on a larger scale to see if your sales improve.
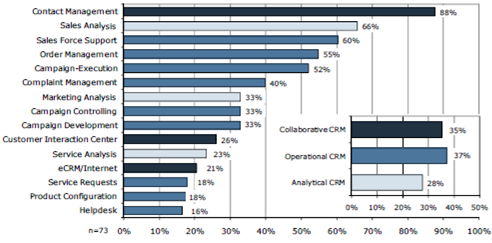
Use of CRM functions in enterprises [1]
How to Conduct CRM Data Analysis
CRM data stores are rich, multi-faceted, and integrated datasets that provide unique insight into a company’s markets, consumers, and sales and marketing activities. These hidden data treasure troves need to be uncovered with the right analyses, but these analyses must be set up properly and optimally from the outset. Treat CRM data processing in an ad hoc manner. It can be difficult to escape any nasty data problems, problematic statistical roadblocks, unanticipated rework, or needless side ventures, all of which can arise if you approach it in an ad hoc manner.
A screenshot of CRM software (source: Internet)
1. Examining the CRM Data’s Facts
The first step in successfully mining the CRM for useful insights and data is to survey the environment by gaining complete access to the CRM system and any online or onsite backup data storage unit where CRM data can be archived. Often consider the extent to which common and potentially relevant data fields are covered (the number of filled out records) and the relationships between the various data tables. Another critical move is to ensure that you are aware of the data’s pathologies.Any reasonably large dataset can contain errors and problems, and CRM data is especially vulnerable because it is mostly entered manually and contains a combination of structured and unstructured data.
2. Combining the Information
To do something worthwhile with the info, put it in a convenient location like a series of interconnected spreadsheets, a range of interconnected tables, or an entire relational database with query and report capability.It involves extracting raw data from the CRM and dealing with data problems that arise from format standardization and data normalization.
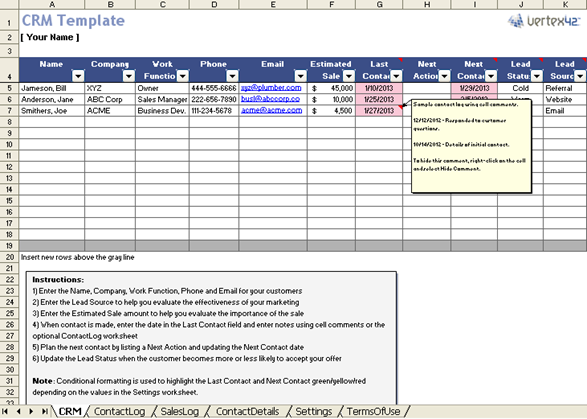
CRM Excel template to save the data for analysis(source: Internet)
3. Mapping Your Research
This is where you gather all of the data and prepare it for the major analysis. It’s one of the most important data mining tasks for figuring out the outcomes.Create a flowchart to help you analyze the results. Because any sufficiently rich dataset will yield millions of possible analyses, it’s critical to concentrate solely on those that can help you achieve your goals.
- Identifying two basic components to lay the groundwork for the study
And if you aren’t certain what kinds of outcomes you want to achieve with the study, it’s always a good idea to consider the following:
1. The amount you’re attempting to assess
2. What you’re attempting to contrast that with
4. Analyzing the Data and Interpreting the findings
Begin analyzing the data mathematical models and data processing scripts until the strategy has been fully planned. Consider the final answers for both of these analyses and refine the estimation measures. Keep based on the proof and the conclusion to prove or disprove, analyze the findings, and stop interpretation paralysis with each completed analysis.
5. Visually Presenting Your Insights
Draw together all of the contradictory findings. More critically, link the dots to form a holistic perspective and a coherent narrative of the insights that truly emerge to impact the study. Depending on the goals and the group you are dealing with, you may opt to be explanatory, instructional, contrarian, visionary, or realistic. There is no shortage of visual aids, immersive material, and digital tools available to help you make your case, but they must be compatible with your storey and the tone you want to project.
6. Other Types of Research in CRM
Other analysis programmes may be commissioned to learn more about the business, your clients, and your own sales activities. Because you will not be analyzing the granular-level, unstructured interactions data, you will need to collect structured data from other sources, such as:
- customer surveys
- lost customers and prospects surveys/interviews
- surveying your own sales team
- commissioning third-party research into your customers and prospects
These ventures will offer quantitative and qualitative data into the clients and sales experience models. They also have an outside-in, unfiltered view that you could not get from just analyzing your CRM results. However, since surveys and interviews are better done with particular objectives in mind, you may need to clarify the questions you attempt to address and shape precise conclusions for the responses before conducting the surveys.Suppose you haven’t formed such strong theories. In that case, it’s better to do a smaller scale exploratory review of the CRM data using the methodology I mentioned since it would be less time-intensive and expensive than actually doing several rounds of consumer and prospect surveys as you refine the hypotheses.
Conclusion
Sales technique is a concretization of sales process measures, and it specifically depicts the direct behaviour of salespeople’s operation in sales processes. When assisted or combined with an appropriate CRM solution, both sales and methodologies are incredibly effective and productive. CRM solutions can be good systems for both management and salespeople, as they concentrate on the automation of sales efficiency and therefore affect sales processes and sales methodology backed [6].In that case, salesperson data capture is used by both sales control and the sales process itself. Salespeople would rather use a product or application that can help them sell more and be more competitive.
References
[1] Michael Torggler, The Functionality and Usage of CRM Systems, World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, 41, 2008, 300-308.
[2]BojanKrajnc, PolonaTominc, Ruben Picek, SimonaSternadZabukovšek, CRM Solutions and Effectiveness of Sales Processes in Export Organizations, Proceedings of the Central European Conference on Information and Intelligent Systems, 29th CECIIS, 2018, 105-112.
[3] Light, B. (2003), “CRM packaged software: a study of organizational experiences”, Business Process Management Journal, Vol. 9 No. 5, pp. 603-616. https://doi.org/10.1108/14637150310496712
[4] Guerola-Navarro, V., Oltra-Badenes, R., Gil-Gomez, H. and Gil-Gomez, J-A. (2020) ‘Customer relationship management (CRM): a bibliometricanalysis’, Int. J. Services Operations and Informatics, Vol. 10, No. 3, pp.242–268.
[5]Gončarovs, Pāvels, Data Analytics in CRM Processes: A Literature Review, Information Technology & Management Science (Sciendo). Dec2017, Vol. 20 Issue 1, p103-108. 6p.
[6] Krajnc, B., Bobek, S., Tominc, P., &SternadZabukovšek, S. (2018). Vplivuporabe CRM informacijskihrešitevnaučinkovitostprodajnegaprocesa. In S. SternadZabukovšek et al. (Eds.), Dinamikaspremembinformacijsketehnologije in informacijskihrešitevterspremembe v poslovnihmodelihpodjetij (pp. 6-43). Maribor: Bio energija.



 Previous Post
Previous Post Next Post
Next Post