
As the data collection methods have extreme influence over the validity of the research outcomes, it is considered as the crucial aspect of the studies
May 2025 | Source: News-Medical
The complexity and data-driven nature of regulatory expectations in modern pharmaceutical R&D is increasing. Today, regulatory agencies, such as FDA, EMA, MHRA, PMDA, and others, expect a clear, consistent, and evidence-based demonstration of efficacy, safety, and benefit–risk of a drug to them. Meeting that expectation has become about more than demonstrating the individual result of a clinical trial- but has leaned heavily towards integrated evidence. Thus, clinical meta-analysis has emerged as one of the most strategic capabilities for not only drug developers, but also the regulatory team. Firstly, a systematic meta-analysis synthesizes data across trials which helps close evidence gaps, and resolve evidence inconsistencies, which all further demonstrates scientifically sound submissions with confidence level expected by regulators.[1]
This article outlines:

Regulatory organizations expect submissions to include three major aspects:
Regulators want:
Regulators evaluate:
Regulators seek:
Where Many Drug Submissions Fail: Common Documentation Gaps
Regulatory reviewers frequently identify shortcomings such as:

Regulatory reviewers frequently ask:
Example Comments from the FDA
When these answers are not available, reviewers may determine that the evidence base is not sufficiently robust, resulting in a CRL (Complete Response Letter), request for additional studies, or non-approval.
Clinical meta-analysis directly addresses the issues regulators most often cite.
Key Concept | Explanation |
Pooling multiple studies | Combine data across several studies in one analysis. |
Minimizes random variability | Reduces errors due to chance or random effects across the individual studies. |
Uncover true underlying treatment effect | A more precise estimate of the true treatment effect. |
Explains heterogeneity between studies | Identifies and quantifies applicable differences in results and characteristics across studies. |
Supports consistent narrative across dossier | Helps maintain a consistent and interpretable story throughout regulatory submission. |
Regulators’ preference for meta-analysis | Regulators prefer meta-analysis because such methods have quantified clarity where studies conflict. |
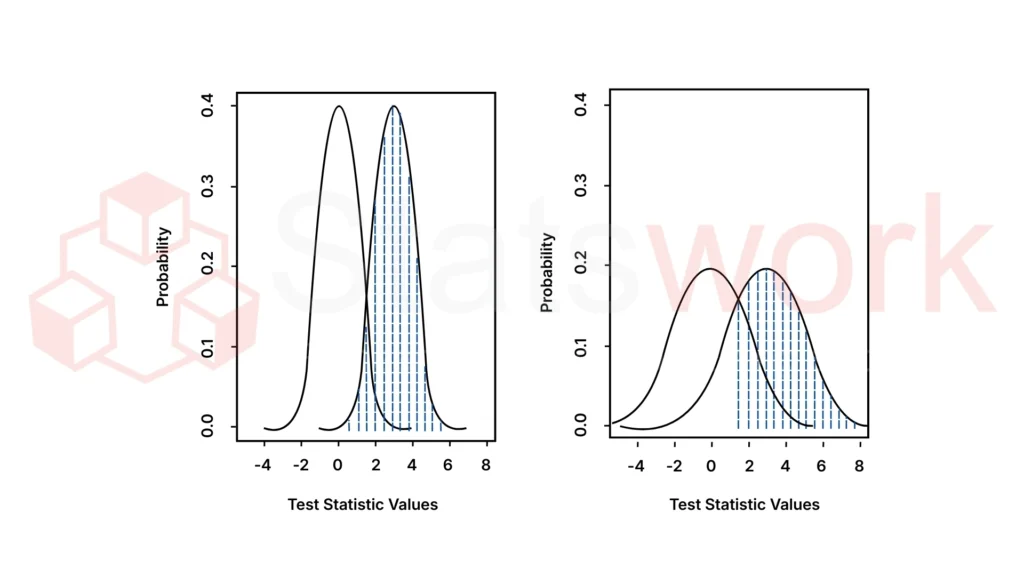
Meta-analysis greatly expands sample size, allowing for:
This becomes particularly important when regulators challenge the strength of a finding based on small or marginal studies.
Practical Considerations:
In drug development, systematic review and meta-analysis have the potential to identify patterns or treatment effects that individual trials fail to detect due to overall lack of power. This ability to one way or another accelerates the identification of effective therapies.[3]
Elements | Provides Important Subgroup Perspectives | Bolsters Safety Assessment |
Focus | Subgroup efficacy, safety, dose-response | Rare adverse events, durability trends, global safety profile |
Key Elements | Subgroup analysis for efficacy, subgroups for safety, dose-response assessment | Rare events, long-term safety, integrated safety assessment |
Regulatory Role | Required as part of ISS/ISE; frequently absent in application | Regulators anticipate an integrated safety assessment rather than cherry picking individual studies |
Contribution | Insightful subgroup perspectives | Strengthens safety profile and reviews potential long-term risks |
Meta-analysis creates a strong, data-driven benefit–risk justification:
Regulatory Need | How Meta-Analysis Helps |
Comparative effectiveness | Enables indirect comparison with standard of care |
Quantifying benefit | Produces a precise estimate of clinical impact |
Safety confidence | Consolidates AE rates across trials |
Risk–benefit balance | Provides an integrated, evidence-based summary |
Shortens Regulatory Queries & Prevents Delays
Meta-analysis pre-emptively answers the most common reviewer comments.
When evidence is proactively integrated, regulators submit fewer clarification questions, reducing back-and-forth cycles and speeding approval.
Example Data
Regulatory approval requires a comprehensive suite of evidence that is strong, consistent, and well-entrenched. Clinical meta-analysis is now considered one of the most powerful methods to secure this evidence and place all of the clinical trials into context:
For pharmaceutical companies integrating meta-analysis early is a competitive advantage but also a regulatory requirement.
If you’re looking to leverage meta-analysis to strengthen your drug development programs or regulatory submissions, Statswork can support you. Our experts conduct advanced meta-analysis tailored for regulatory success, enabling faster approvals and smarter decision-making.
WhatsApp us