
As the data collection methods have extreme influence over the validity of the research outcomes, it is considered as the crucial aspect of the studies
May 2025 | Source: News-Medical
In 2025, organizations are standing at a crossroads between manual data entry and automated data entry solutions. The solution to this issue is going to depend on the type of data, size of the project, accuracy requirements, and budget. By weighing the pros and cons of manual vs automated data entry, organizations can make more educated decisions about their own workflows. The comparison below is intended to help you find the best data entry solution for your organization.
Manual data entry consists of human agents copying data from either physical documents or digital files into more structured formats like spreadsheets or databases. Although manual data entry is slower than automated methods, some businesses may find significant advantages.
Automated data entry leverages technologies like OCR (Optical Character Recognition), AI, and machine learning to process and input data at scale. This method is faster and more efficient than manual entry but requires upfront investment.
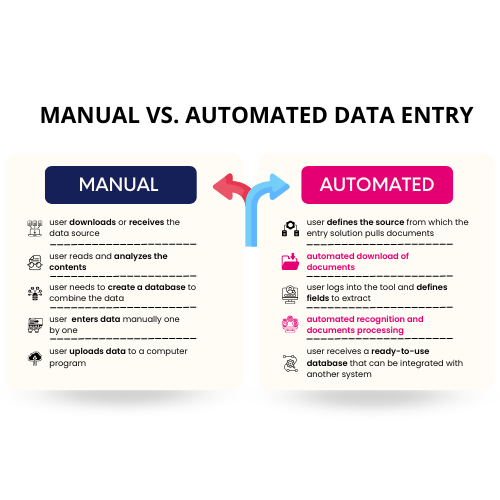
The decision on which data entry method to adopt depends largely on the specific requirements of your business and the nature of the project. Some important factors to consider are:
In contemporary B2B processes, automated and manual data entry have distinct functions. Manual data entry has advantages for manual data entry like tasks that require detail and perception, or when human insight adds value. Automated data entry works best for repetitive, bulk activities where speed and accuracy is important. Many organizations find that a hybrid model (using both manual and automated data entry) provides the best of both worlds when seeking flexibility and productivity.
Statswork offers customized data entry automation services to meet the needs of your business. If your business needs to improve B2B data management, automate web data extraction, or grow your data workflows. To learn how we can work together to implement the best data entry solutions for your company, get in touch with us right now.
WhatsApp us